Innovating Pharmacy Education: Preparing Future-Ready Pharmacists through Integrated Learning
“At the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University, the Pharmacy Integrated Learning (PIL) course is a six-year strategy that integrates practice, people, and innovation from students’ first semester through graduation. Each stage builds progressively: alumni mentorship in Year 1, empathy through role-reversal in Year 2, design thinking and innovation challenges in Year 3, and senior projects and diverse internships from Year 4–6, where students contribute meaningful outputs while developing adaptability and leadership.
Technology enhances this journey through ChulaMOOC for lifelong learning, CUDSON for soft-skill self-assessment, and progressive AI literacy training. The impact is evident in students winning national innovation competitions, graduates succeeding across diverse career paths, and faculty receiving teaching awards.
Aligned with Chulalongkorn’s vision and strategic growths, PIL is beyond a curriculum—it is a transformative framework that nurtures knowledge, professional and future skills, ethics, and workplace readiness, producing future-ready pharmacists who contribute meaningfully to healthcare and society.”
At the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University, our signature teaching and learning strategy in pharmacy education is the Pharmacy Integrated Learning (PIL) course, a six-year longitudinal program that connects students with practice, people, and innovation from their first semester until graduation. Designed to nurture professional identity, empathy, creativity, and workplace readiness, PIL embodies our mission to create ethical leaders, promote lifelong learning, and generate impactful knowledge.
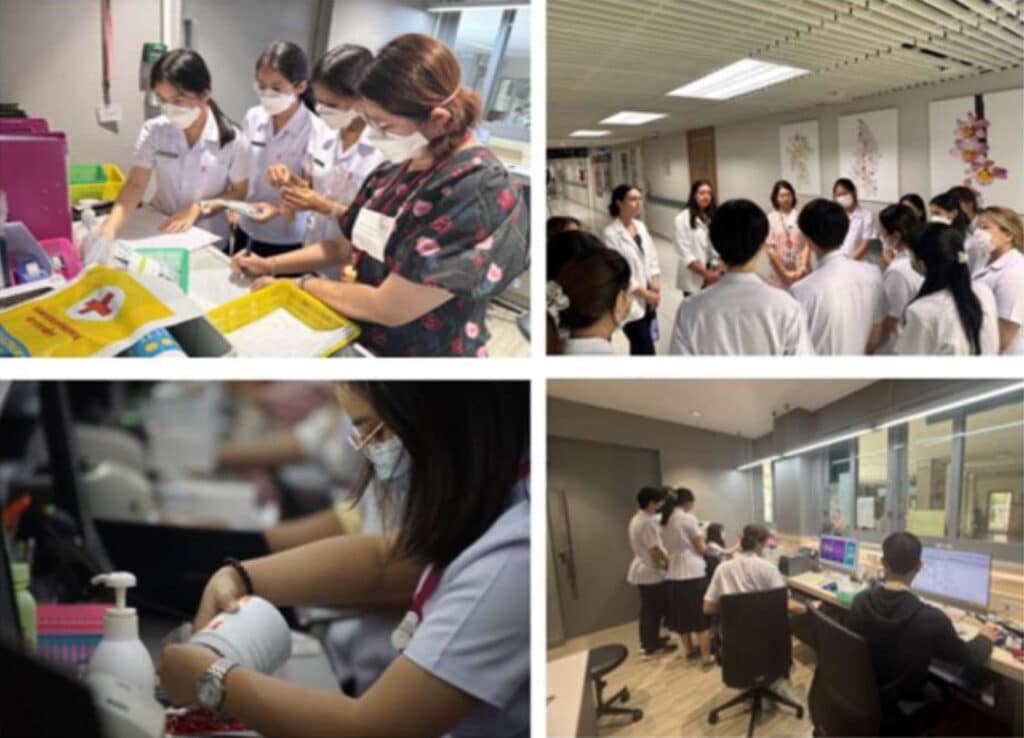
The PIL series are structured as a developmental journey along with other academic and professional practice courses. In the first year, students conduct structured interviews with alumni and practitioners, replacing traditional lectures with authentic mentorship encounters that inspire professional aspiration. In the second year, they role-play as patients in community pharmacies and then respond as pharmacists, a role-reversal that fosters empathy, communication, and patient-centered thinking. By the third year, they shift toward creativity and innovation, applying design thinking to develop new pharmaceutical concepts and presenting them in peer-voted competitions that simulate real-world funding decisions. Many of these ideas are carried forward into senior projects in Years 4–5, where students conduct hypothesis-driven research, from literature review to experimentation and analysis, building critical thinking and evidence-based practice skills. In Years 4–6, students transition into real-world practice through internships in hospitals, community pharmacies, manufacturing plants, and pharmaceutical companies, where they contribute meaningful outputs such as patient education materials and strategic planning while developing adaptability, leadership, and professional mastery.
University-supported technology is integrated to enrich the learning journey. ChulaMOOC provides access to courses that broaden perspectives and promote lifelong learning. CUDSON, a soft-skill self-assessment platform, enables students to track growth in communication, teamwork, and empathy yearly, while faculty use the results to guide development. In parallel, AI literacy is integrated progressively from foundational awareness to advanced applications, ensuring graduates are equipped for a technology-driven healthcare landscape.
The impact of this approach is evident in students’ achievements, including sweeping top prizes at the ISPE Hackathon and winning the Innovators Impact Challenge with projects directly stemming from PIL’s design thinking exercises. Graduates consistently enter diverse career pathways across hospitals, community practice, industry, and entrepreneurial ventures. Faculty excellence is recognized at institutional level, with two members receiving prestigious Excellence in Teaching Awards, while systemic support is sustained through regular training workshops and site visits, ensuring that both academic and experiential teaching remain current, innovative, and collaborative.
The strategy prepares students for five essential dimensions: basic knowledge acquisition, professional skills development, future skills cultivation (empathy and teamwork), ethics fulfillment, and employment readiness. Students benefit from learning environments co-created with alumni, practitioners, and faculty, where teaching excellence is continuously improved. This framework enables graduates to thrive as competent, adaptable pharmacists contributing meaningfully to society.
In conclusion, PIL, Pharmacy Integrated Learning, is more than a curriculum innovation—it is a signature teaching and learning strategy that integrates real-world experiences, innovation, and empathy across six years. It prepares students to be mastery leaders in pharmacy and healthcare, and reflects our institution’s commitment to distinctive, impactful higher education.
By Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chulalongkorn University
Others
Improving Teachers’ Digital Literacy
Chula Faculty of Engineering Partners with Learn Education to Improve Teachers’ Digital Literacy