Thai Red Cross Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Centre (EID): A Mission of Research, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases in Service of Humanity
In the past decade, the world has faced with various emerging diseases that has increased in its destruction power since the Sika , Ebola, Mers, and most recently, the Corona virus that the humanity is dealing with right now. With more than 219 million people infected and 4.55 million deaths, one of the reasons that allows this virus to become widespread is the globalization. This lies in the limitlessness of technology and transportation which allows people to travel easily that has boosted the travel industry especially in Thailand.
Thailand, one of the tourist destinations of travellers all around the world, would then faced with risks of infection carried by globalization and travel. The information from the tourist and sport ministry has shown that the past 3-4 years prior to the pandemic, Thailand has an average of more than 30 million tourists visiting annually, out of which some could be the disease carrier. Close monitoring of new disease is therefore one of the most important mission that Thai health officials will have to deal and recognize its impact. It is necessary to create a network of collaboration which leads to effective preparation of prevention or control of emerging diseases to minimize its impact.

The faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, has therefore, established The Thai Red Cross Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Centre [ https://chulalongkornhospital.go.th/kcmh/en/ec/thai-red-cross-emerging-infectious-diseases-health-science-centre/ ] in 2016 , which works hang in hang with the World Health Organization in research and host conferences of infectious disease between human and animals to actively target the source of infection (upstream operation) and prepare to cope with the risks of emerging virus outbreak alongside with global collaborations. This centre is vital to help Thailand in dealing with the Covid-19 Pandemic from aid of Bureau of Epidemiology, Department of Disease Control to allow in identifying and confirming infected patients by identifying viral DNA and providing such information to the health ministry for prevention of outbreak.

Prof.Dr. Teerawat Hemachuta, head of The Thai Red Cross Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Centre, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn university, and a member of the WHO Expert Advisory Panel on Rabies and WHO member of the International Health Regulations Roster of Experts as an expert in Human-animal interface (Zoonoses) stated that “The root causes of human diseases, 70% comes from animal and there are our 500,000 viruses that we couldn’t identify which could further develop in infecting humans and emerge as emerging virus. Therefore, the research and active search to identifying which animal could carry which type of diseases would allow us to compare and risks of the locations of the root of disease. This could lead to protective measures in preventing an outbreak and accurately identifying at risk zones.
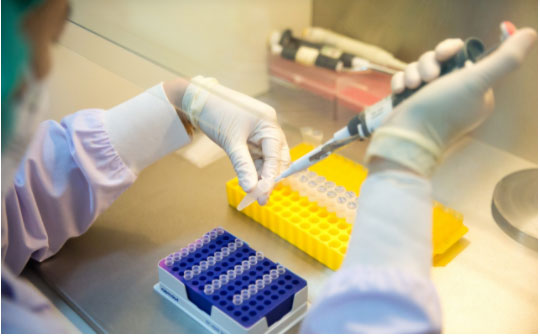
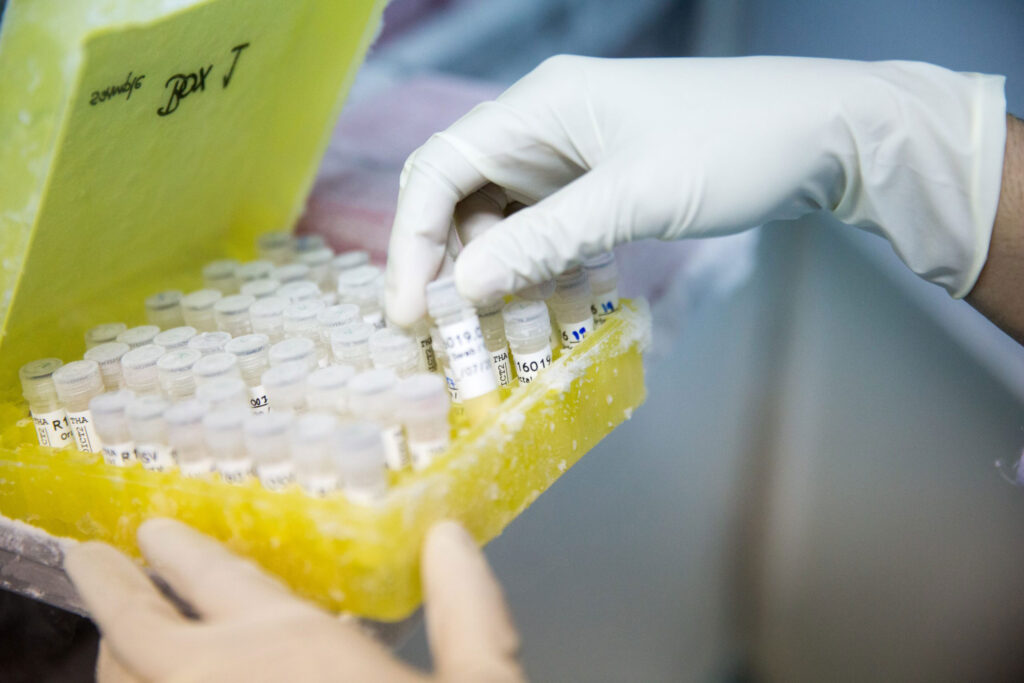
The development of emerging virus active facilitation of The Thai Red Cross Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Centre is a result from continuous collaborations in domestic and international levels.
1) World Health Organization: Supporting the work of the World Health Organization on research and diagnostic testing confirming infectious diseases from animals to humans while also offering advice and organizing workshops, as an expert director, for participating countries of WHO – Regional Office for South-East Asia, which is comprised of 11 countries including Bangladesh, Bhutan, South Korea, India, Indonesia, Maldives, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Timor-Leste, and Thailand.
2) United States Agency for International Development (USAID): creating international emerging disease research networks through the research project PREDICT, developing laboratory abilities to be an innovation in the diagnosis of new viral infectious diseases and detection of infected patients with an unknown cause such as applied laboratories to detect the COVID-19 virus.
3) United States Department of Defense: developing research and emerging disease laboratories as well as all-round scientific tools for research, diagnosis, and surveillance of disease such as Infectious Disease Sample Bank, Virus Bank, diagnosis with a molecular biology approach, virus genetic decoding, virus culture for diagnosis, and creating Clinical Genomics Integration Platform, etc.
4) Ministry of Public Health Thailand: expand national research into local communities by developing diagnosis of Zika virus from samples other than blood and urine including breast milk, placenta, amniotic fluid, brain membranes, semen, saliva, and tears.
The cautious facilitation of emerging virus by The Thai Red Cross Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Centre, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University and allies, has innovated the working process of Thai medical personnels and provide cautious measures in handling of emerging virus COVID-19 along with preventative plans and identifying risky locations with accuracy. Until, the team has developed COVID-19 test kit, that develops from the idea of searching of COVID-19 protein fragments and other signs of infections from other proteins in saliva and other means. The identification process is used with Mass Spectrometry that can identify a large mass of virus with little time. This machine could identify viral protein and related protein from both normal strain as well as the Indian, English, South African strain with more precision compare to PCR from samples of nasal swab or throat swab. This could be used as an instrument of identifying infection, with efficient steps in collecting samples such as saliva as well as cost efficient in using with large population such as uses in industrial offices or large corporations.
In addition, the EID also provides academic services by supporting the Ministry of Public Health, the Global Network of the World Health Organization (WHO), and World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) in various dimensions of research, diagnosis, treatment, and control of new emerging diseases and neurological diseases, including:
- Collaborating in disease investigations with the Ministry of Public Health when there are outbreaks of unknown causes.
- Conducting research and developing diagnostic tools for neurodegenerative diseases to support changes resulting from an aging society.
- Participating in the creation of disease care manuals, medical practices, and diagnostic guidelines.
- Serving as a committee/expert for the Ministry of Public Health, the World Health Organization (WHO), and the Asia-Pacific region.
- Organizing practical training programs to disseminate knowledge to both academic and public audiences.
- Delivering lectures and knowledge to external organizations.
- Developing a website to disseminate knowledge and understanding of emerging diseases. [ https://www.trceid.org/home ]


BY
- Thai Red Cross Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Centre
- Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University
Related articles:
Others
Enjoy Music at Chula
Thai and Western, traditional and contemporary offerings find a large and enthusiastic audience